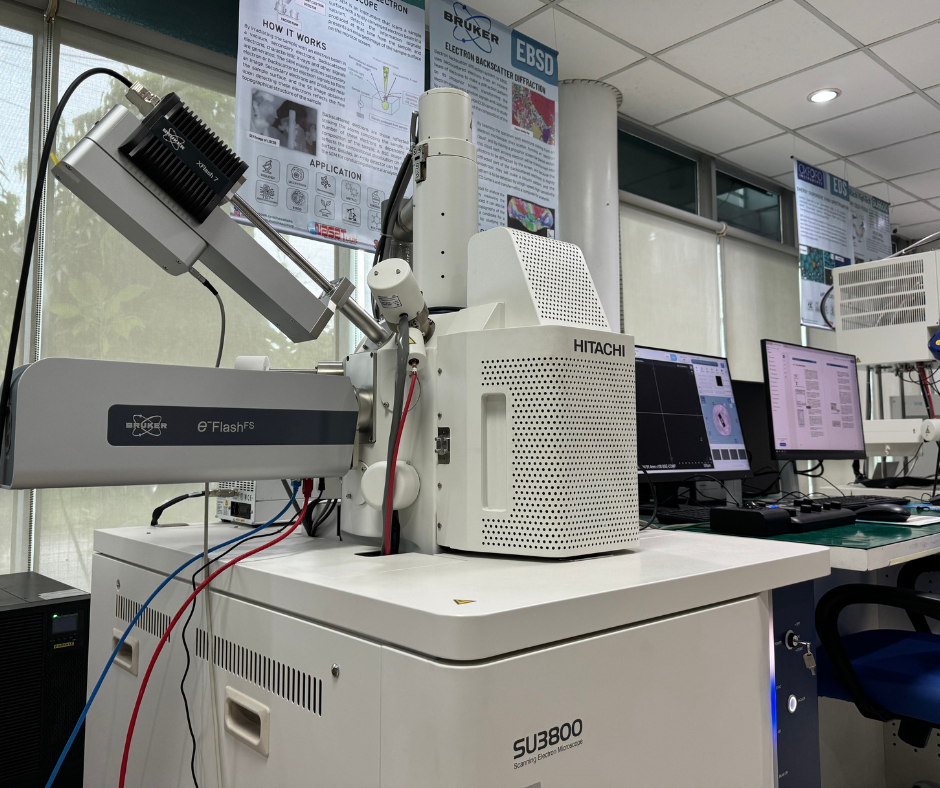
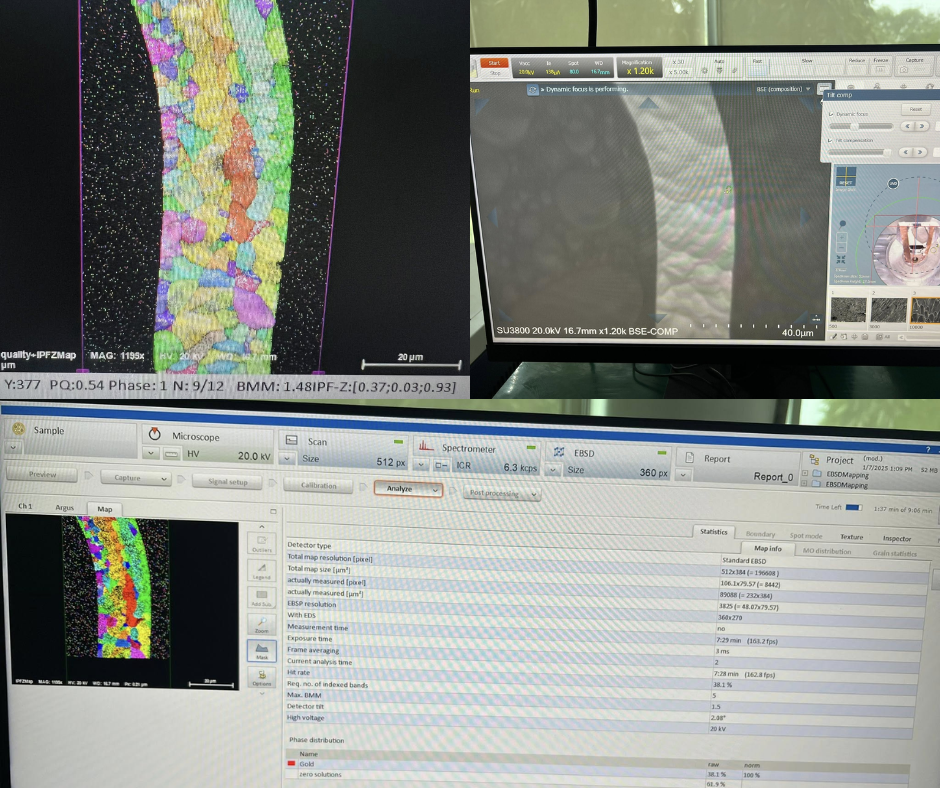
Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) is a microstructural characterization technique used in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to determine the crystallographic orientation, phase distribution, and grain boundary characteristics of crystalline materials. EBSD works by detecting diffraction patterns formed when an electron beam interacts with a tilted sample surface.
This method is widely applied in materials science, metallurgy, geology, and semiconductor research. It provides critical insights into grain size, texture, deformation mechanisms, and phase identification, supporting both fundamental research and industrial quality control.