Service Details
X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (XRF) is a non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. It works by measuring the characteristic secondary (fluorescent) X-rays emitted from a sample when excited by a primary X-ray source.
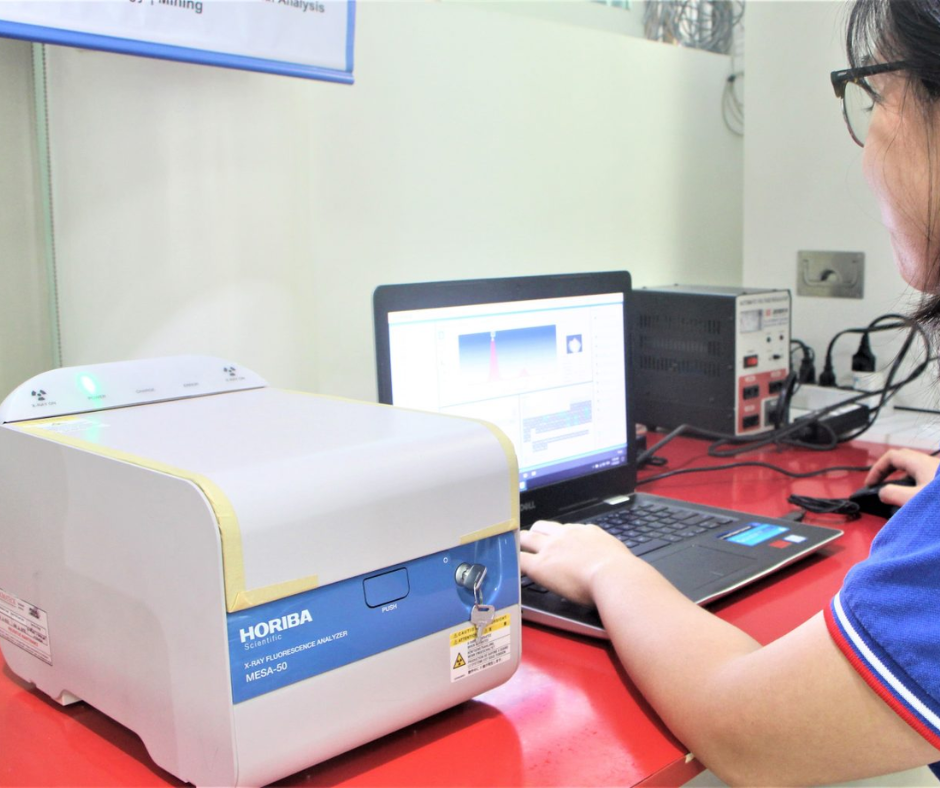
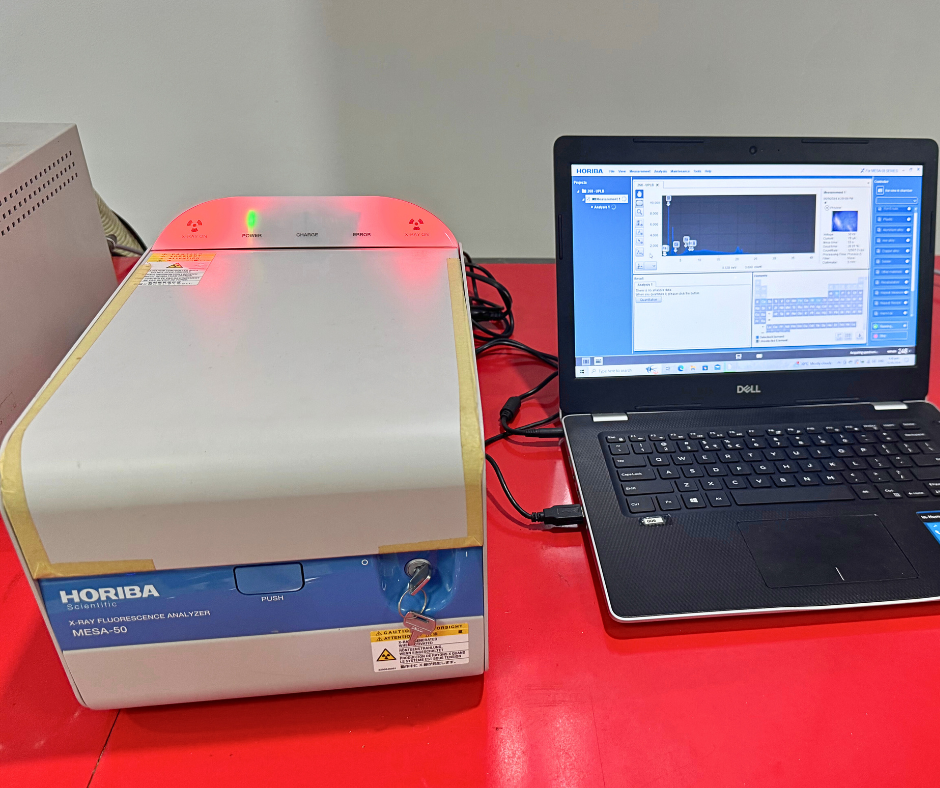
At NASAT Labs, our XRF analysis services in the Philippines utilize the HORIBA MESA-50, capable of detecting elements from sodium (Na) to uranium (U). This technique supports rapid, accurate analysis of solids, liquids, powders, and thin films with minimal sample preparation. XRF is ideal for metals, minerals, polymers, ceramics, and more—making it a powerful tool for material identification, quality control, and environmental monitoring.
Common Applications
- Art & Archaeology
Analyzes pigments, artifacts, and historical materials without damaging samples
- RoHS Compliance Screening
Detects restricted substances (e.g., Pb, Cd, Hg, Br) in electronics and consumer products.
- Metals & Alloys
Determines elemental composition for quality control, alloy verification, and process monitoring
- Geology & Mining
Analyzes rocks, ores, and sediments for mineral exploration and resource mapping
- Environmental Science
Detects pollutants in soil, water, and air; supports contamination studies and remediation
- Polymers & Plastics
Measures additive concentrations and ensures compliance with safety standards
- Cement, Glass & Ceramics
Monitors raw materials and final products for consistent composition and performance
- Petrochemicals
Screens crude oil and fuels for trace elements like sulfur and vanadium
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
Verifies raw materials and finished products; supports medical device analysis
- Forensic Science
Examines trace evidence such as gunshot residue, inks, and tool marks
- Additive Manufacturing
Evaluates powder quality and composition for 3D printing applications
- And much more.
XRF is a versatile tool for fast, accurate elemental analysis across research and industry.