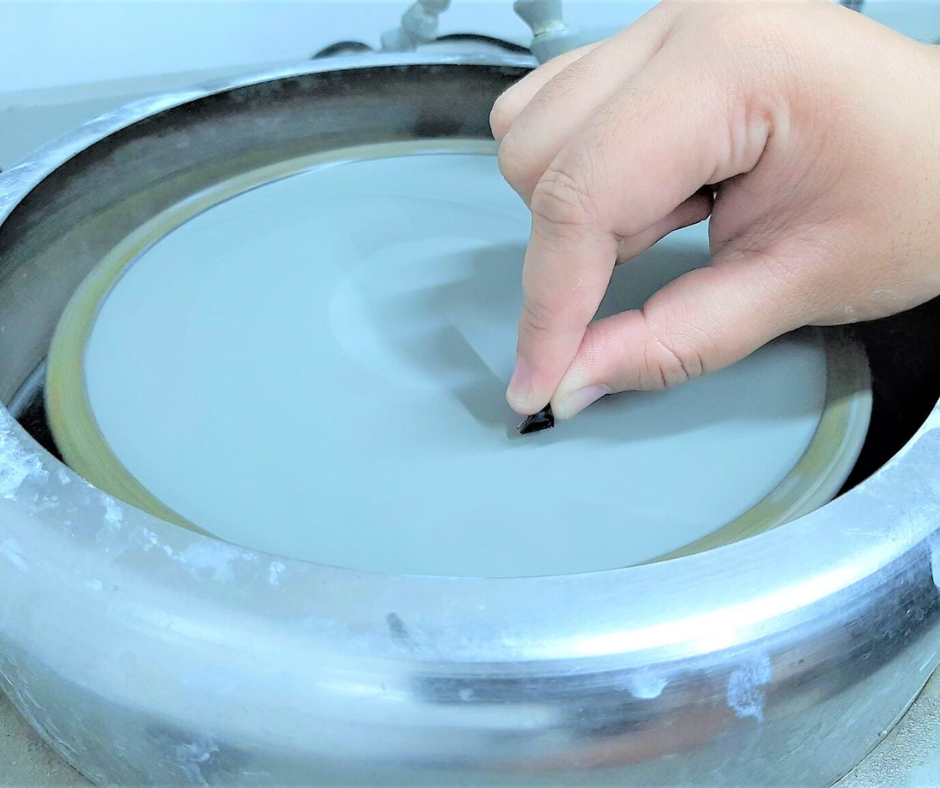
Mechanical cross sectioning is a sample preparation technique used to expose internal structures of materials and devices by physically cutting through them. This method is essential for examining layer interfaces, defects, and structural integrity in components such as PCBs, semiconductors, and multilayer materials.
The process typically involves precision cutting, grinding, and polishing to produce a clean, flat cross-sectional surface suitable for imaging and analysis using SEM, EDS, EBSD, and optical microscopy. It is widely used in failure analysis, quality control, and materials research.