Service Details
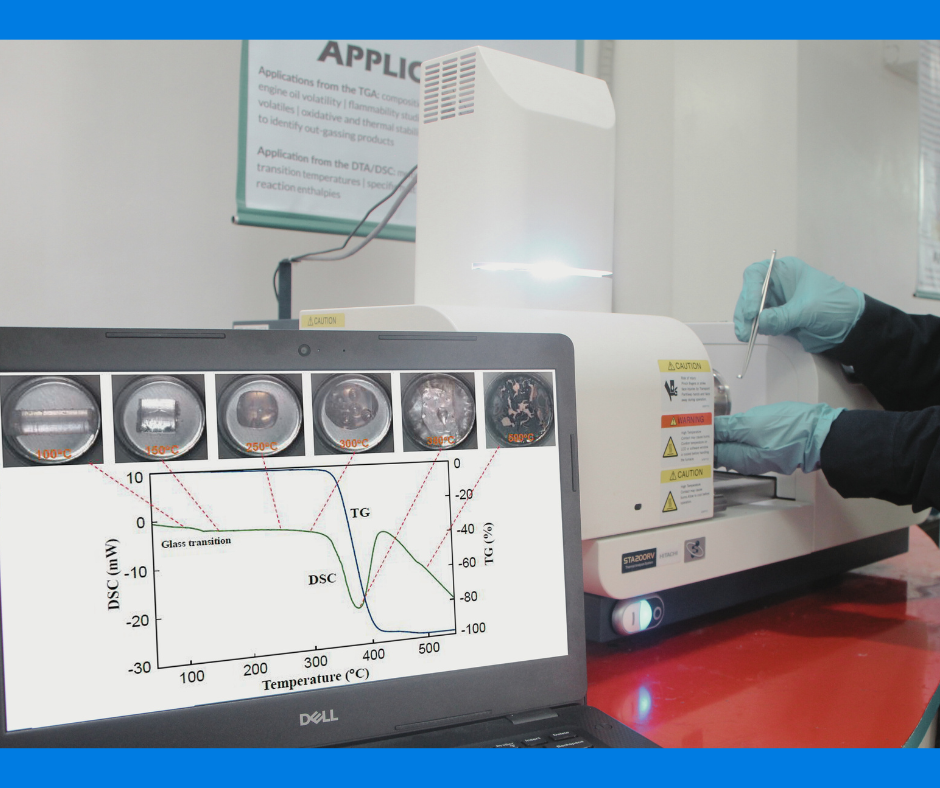
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) is a thermal analysis technique used to measure heat flow associated with material transitions as a function of temperature. It provides insights into melting points, glass transition temperatures (Tg), crystallization behavior, and thermal stability.
DSC is widely used in research and industry to characterize polymers, pharmaceuticals, food products, and metals. The technique helps identify phase transitions, assess material purity, and evaluate compatibility in formulations. It is suitable for solids, liquids, and powders.
Common Applications
- Polymer Development
Determines Tg, melting point, and crystallization behavior for material optimization
- Pharmaceuticals
Assesses thermal stability and compatibility of drug formulations
- Food Science
Analyzes melting, freezing, and crystallization in food products for processing and storage
- Quality Control
Evaluates consistency and thermal properties of materials across batches
- Material Testing
Studies thermal behavior of metals, ceramics, and composites
- Oxidation Stability
Measures oxidation induction time (OIT) for polymers and oils
- And much more.
DSC supports research, development, and quality assurance across diverse industries.